Overview
Technology as a Service, such as iPaaS and PaaS have become key drivers in propelling businesses toward digital expansion. PaaS solutions enable organizations to manage the entire lifecycle of application development, empowering developers to create applications directly in the cloud. Concurrently, iPaaS stands out as a modern cloud integration solution, offering API-driven software connections and centralizing the integration of systems, data, and processes for businesses.
This article invites readers to explore the nuances of these cloud-based services, providing a clear comparison of their differences and illustrating how each contributes to the digital landscape.
What is iPaas?
In the rapidly evolving digital landscape, the importance of Integration Platform as a Service (iPaaS) roles has surged. iPaaS serves as a cloud-based platform, empowering organizations to develop, execute, and govern integration flows. These flows seamlessly connect a mix of on-premises and cloud-based processes, services, applications, and data across multiple organizations. The adaptability and scalability of iPaaS solutions make them indispensable in today’s interconnected world.
While it depends on the vendor, an iPaaS solution generally has this key component
- Connectivity: At its core, iPaaS fosters connectivity, enabling various applications to communicate and collaborate effortlessly, bridging the gap between disparate systems.
- Application Integration: This crucial component orchestrates the logic for data exchange between apps, handling the routing and orchestration of data to ensure timely and accurate delivery.
- Data Integration: iPaaS solutions excel in mapping sender and receiver data objects. This meticulous mapping guarantees the seamless association of data across different environments, simplifying complex integrations.
- API Management: Managing APIs is vital in the integration process, and iPaaS platforms offer robust tools for API governance. This ensures that APIs remain secure, efficient, and in compliance with business policies.
- Monitoring: Monitoring capabilities within iPaaS platforms offer unparalleled visibility into integrations. This feature is key for troubleshooting and debugging, enabling organizations to maintain smooth operational flows.
Read more about the Definition of iPaaS here: What is iPaaS? The Complete Guide for Beginners to easily imagine how iPaaS activates the operation, let’s take a look at this use case.
Use case
By connecting your ERP (enterprise resource planning) system with your CRM, your finance team can automatically sync customer-related fields between the two, which speeds up all kinds of finance workflows and prevents costly human errors.
For example, with iPaaS solution providers like Beehexa, you can integrate Acumatica with a CRM like Shopify and then implement a sync where every new Shopify order, product, or customer creates an identical one in Acumatica.
With this integration in place, you can
- Save a lot of time: Shopify eCommerce integrations will synchronize into categories according to their common characteristics, pricing, etc.
- Improve business efficiency: Increase sales and revenue by modifying your sales strategy more successfully, preventing expired inventory or a shortage of products.
- Enhance customer experience: ERP integration is essential since it completes all tasks faster.
What is PaaS?
Platform as a Service (PaaS) is a cloud computing model provided by third parties that supplies the software and hardware needed for application development. This service allows organizations to create, operate, and manage applications without the burden of underlying infrastructure maintenance. As the digital age ushers in a deluge of new technologies and data, traditional systems struggle to keep pace. The shift towards cloud infrastructure, including PaaS, addresses the challenges of modern business demands. It offers a cost-effective and simpler alternative to purchasing, installing, and managing hardware and software on-premises.
Like IaaS, PaaS includes infrastructure—servers, storage, and networking—but also middleware, development tools, business intelligence (BI) services, database management systems, and more. PaaS is designed to support the complete web application lifecycle: building, testing, deploying, managing, and updating.
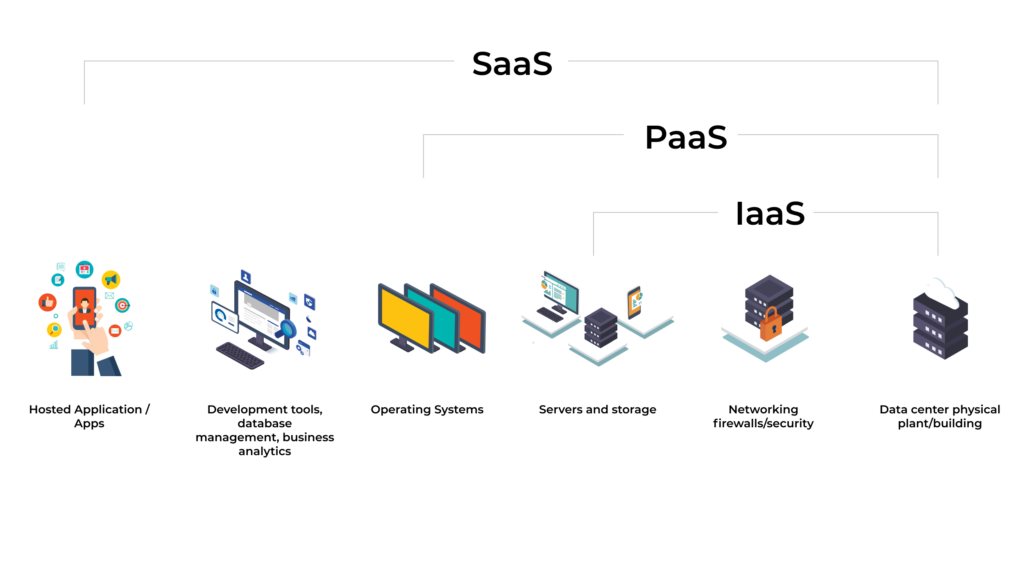
Key Components of PaaS:
- Development Tools: Web-accessible tools for creating software, including IDEs and code editors.
- Middleware: Facilitates app communication and data management.
- Operating Systems: Manages OS compatibility and security updates.
- Database Management: Offers systems for efficient data handling without the need for extensive administration.
- Infrastructure: Automatically managed servers, storage, and networking.
- Security: Implements measures like data encryption and secure access to protect applications.
- Integration: Supports connections with external services and APIs for enhanced app functionality.
PaaS enables rapid application development and deployment by handling the underlying infrastructure, offering scalability, and ensuring security, thereby allowing developers to focus on building high-quality applications.
Use case
Let’s look at some of the leading providers of PaaS.
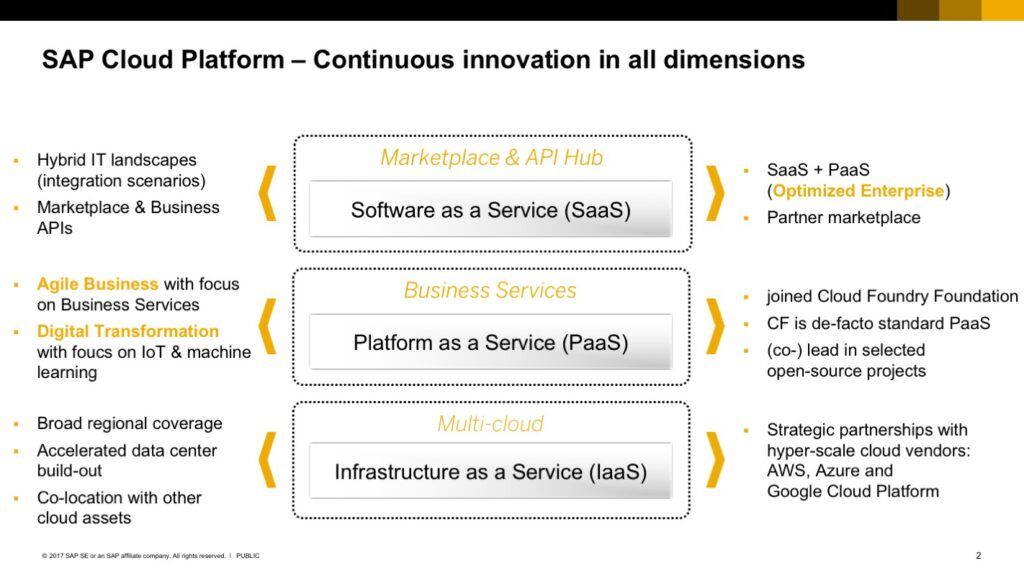
- SAP Cloud Platform: SAP’s cloud PaaS offers an open platform for easy app deployment, integrating cloud and on-premise solutions with over 1,300 built-in apps. It streamlines application development with a comprehensive range of services.
- Microsoft Azure: Azure provides a PaaS environment that supports the full web app development cycle and is compatible with various languages and frameworks. It offers a wide range of cloud services and spans SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS, accommodating all cloud computing needs.
Advantages of iPaaS and PaaS Solutions
Scalability
- PaaS: Providers like SAP Cloud and Red Hat OpenShift offer flexible pay-as-you-go plans, allowing businesses to scale resources according to their needs, and optimizing costs.
- iPaaS: Tailored for growth, iPaaS solutions facilitate easy addition of integrations, supporting both cloud and on-premises resources, ensuring seamless expansion even with legacy systems in place.
Cost Efficiency
- PaaS: Reduces expenses associated with building and maintaining on-premises infrastructure, though development costs for app integrations remain.
- iPaaS: Despite a higher upfront cost, iPaaS can lower overall expenses with its flexible integrations and pre-built connectors, making custom integration accessible to non-technical staff and reducing manual data handling.
Improved Time to Market
- PaaS: Eliminating infrastructure management allows teams to focus on development and deployment, speeding up the release of new apps.
- iPaaS: Streamlines the integration of new applications and systems, enhancing collaboration across engineering, testing, and marketing teams, thus accelerating product launches.
Enhanced Security
- PaaS: Selecting a provider with strong security measures ensures the protection of code and data, with features like encryption and backup solutions.
- iPaaS: Offers robust security protocols, including encryption and compliance aids like access control and activity logging, minimizing risks associated with human error and aligning with industry regulations.
Conclusion
iPaaS and PaaS platforms offer substantial benefits as cloud-based services managed by external vendors, surpassing traditional in-house systems in terms of scalability, cost savings, market responsiveness, and security. Yet, they serve distinct purposes. PaaS provides organizations with the tools to oversee the entire application development lifecycle internally. In contrast, iPaaS enables the integration of various cloud-based and on-premises applications, catering to diverse organizational integration needs.
Ready to try an out-of-the-box iPaaS solution? Feel free to contact HexaSync, share your requirements, and explore how our platform can transform your organization’s integration landscape. Contact HexaSync today and begin your journey towards seamless integration!