Cloud integration is the key to modern business efficiency, enabling seamless connectivity between cloud-based and on-premises systems. This process ensures smooth data sharing and system communication, which is essential for operational agility and innovation. In this article, let’s discuss cloud integration, discover its benefits, and find ways to adopt it.
What is cloud integration?

Cloud integration connects multiple cloud services (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS, iPaaS, machine learning, data analytics, etc.) and on-premises systems to facilitate real-time seamless business data and process exchanges. For example, if you have a retail store and an online store, they are separate operations, but you only have an inventory. It will take a lot of time to manually adjust and manage your stock. However, if you connect them, whenever an item is sold online, the eCommerce platform automatically updates the inventory database in real time.
This approach boosts operational efficiency, enhances data access, and simplifies workflows by harmonizing computing resources, applications, and storage solutions. Vital for achieving agility and scalability, cloud integration is key to driving digital transformation and innovation in the modern, cloud-focused business landscape.
Is cloud integration a better option than on-premise?

Cloud integration and on-premise systems are fundamental to managing business operations and data. Each comes with distinct advantages and disadvantages, catering to different business needs and priorities.
Benefits of cloud integration
Cloud integration offers significant advantages for businesses, streamlining operations and fostering growth. Here are the key benefits:
- Scalability and flexibility: Easily adjust resources to meet changing demands without major upfront investments.
- Cost efficiency: shift from capital expenditure to operational, with reduced costs for maintenance and upgrades managed by the provider.
- Improved collaboration: enables remote access to data and applications, supporting workforce mobility and global teamwork.
- Faster time-to-market: Rapid deployment capabilities accelerate responses to market changes and innovation opportunities.
- Enhanced security and compliance: Benefit from advanced security measures and compliance with global standards, reducing the risk of data breaches.
- Disaster recovery: cloud-based backup and recovery solutions ensure business continuity in the event of data loss incidents.
- Streamlined IT management: Offloads routine IT tasks to the provider, allowing internal teams to focus on strategic initiatives.
- Access to advanced technologies: Provides access to the latest in AI, machine learning, and analytics without significant investment.
Cloud integration vs On-premise
Cloud integration utilizes internet-hosted services for scalable, cost-effective, and accessible data management, while on-premise systems use company-owned infrastructure for greater data control and security, with higher initial costs and maintenance requirements.
Here’s a concise table comparing the key differences between cloud integration and on-premise systems:
| Feature | Cloud Integration | On-Premise |
| Initial Cost | Lower upfront costs as it operates on a subscription model. | Higher upfront costs for infrastructure and licensing. |
| Operational Expense | Costs are operational, based on usage. | Capital expenses dominate, with ongoing operational costs for maintenance. |
| Scalability | Highly scalable, with resources adjustable according to demand. | Scalability is limited by existing infrastructure; upgrades require additional capital investment. |
| Maintenance | Maintenance and updates are managed by the provider. | Requires in-house IT staff for maintenance and updates. |
| Security | High-level security measures are provided, though dependent on the provider. | Direct control over security measures is potentially more customizable. |
| Compliance and | Dependent on the provider’s adherence to standards. | Full control over compliance measures. |
| Remote Accessibility | Easily accessible from anywhere with internet access. | Accessibility is limited, often requiring additional setup for remote access. |
| Data Control | Data is stored off-site, with control shared with the provider. | Full control over data storage and management. |
| Customization | Some limitations, depending on the platform. | Highly customizable to specific business needs. |
| Disaster Recovery | Typically included, with robust backup solutions. | Requires separate planning and investment in backup and disaster recovery solutions. |
| Dependency on the Internet | High, as services are accessed over the internet. | Less dependency, with most resources accessible on the local network. |
| Vendor Lock-in | Potential risk of dependency on specific cloud services and tools. | No vendor lock-in for cloud services, but there is potential for hardware/software dependencies. |
Types of cloud integration
Businesses can adopt diverse cloud integration strategies to refine their IT infrastructure, boost efficiency, and foster innovation. Key among these are Multi-Cloud Integration, Hybrid Integration, and Integration Platform as a Service (iPaaS). Each approach serves distinct organizational requirements and objectives, presenting specific advantages and challenges.
Multi-cloud integration
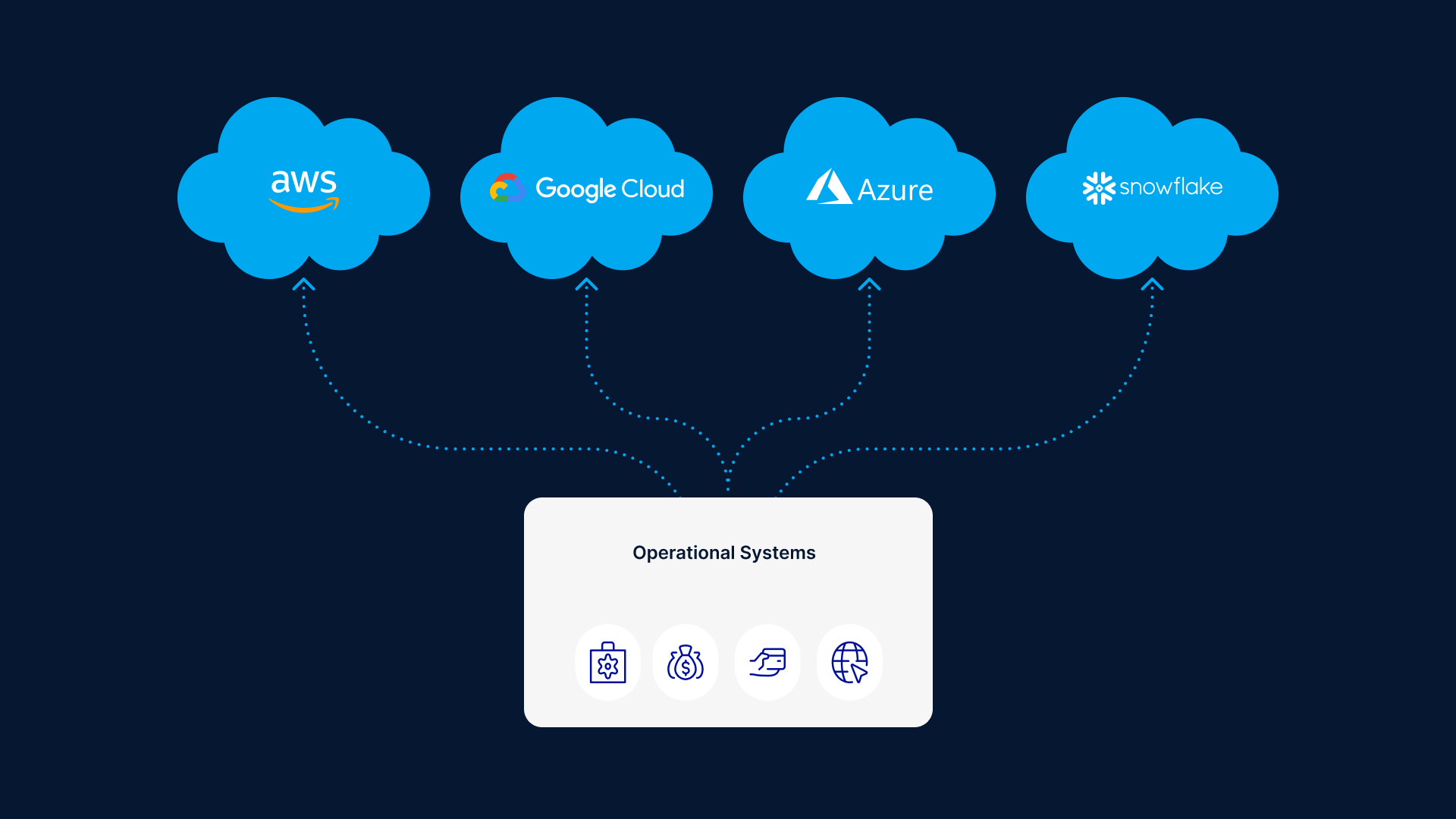
Multi-cloud integration involves leveraging a combination of cloud services from various providers to create a comprehensive, agile, and resilient IT infrastructure. This strategy allows businesses to optimize their resources by selecting the best services from different vendors, thereby avoiding vendor lock-in, enhancing disaster recovery plans, and ensuring service compliance with regional regulations.
An example of multi-cloud integration is seen in enterprises that utilize AWS for its advanced machine learning and analytics capabilities, Google Cloud for its strength in containerization and Kubernetes management, and Microsoft Azure for its seamless integration with existing Windows-based infrastructure and enterprise applications.
Hybrid integration
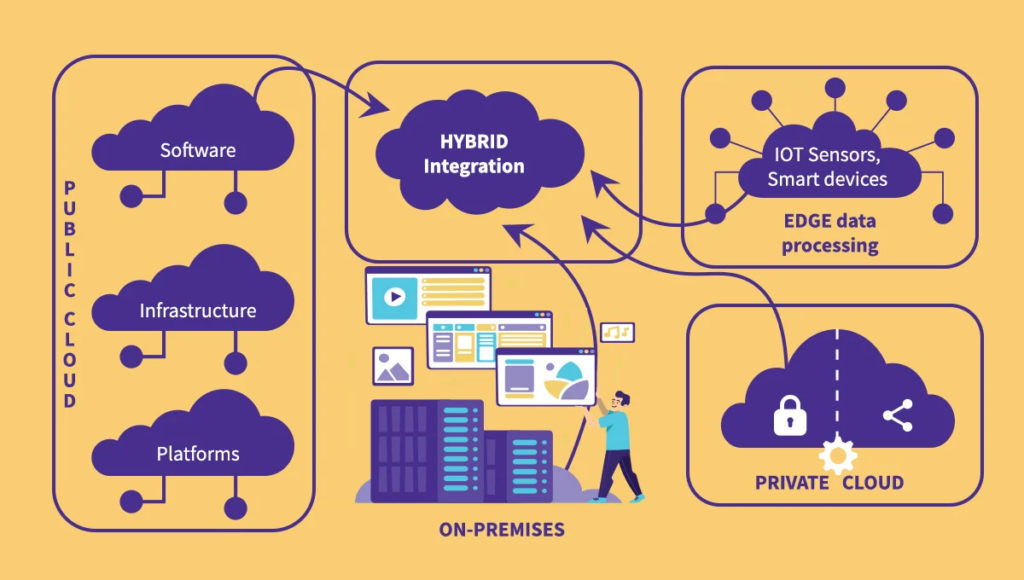
Hybrid integration combines on-premise systems and cloud services, delivering both security and control with cloud scalability and flexibility. It secures data management and leverages cloud advantages for better analysis and service, offering a balanced solution for contemporary IT demands.
A tangible example of hybrid integration can be found in financial institutions that maintain sensitive customer data on-premise for compliance and security while using cloud-based analytics and customer relationship management (CRM) services to enhance operational efficiency and customer service.
Integration platform as a service (iPaaS)
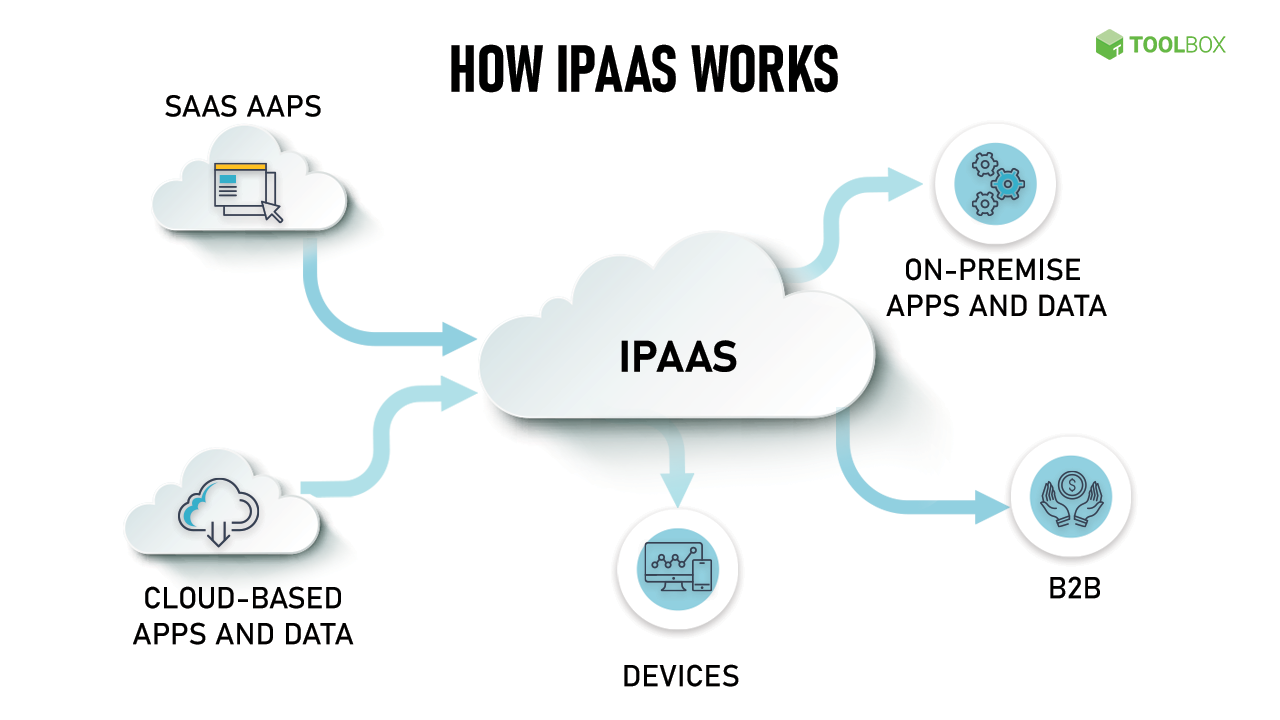
Integration Platform as a Service (iPaaS) streamlines the connection of applications, data, and processes across cloud and on-premise environments. It offers automation tools, connectors, and workflows for easy data exchange and coordination, reducing the need for complex coding. iPaaS accelerates digital transformation and boosts organizational efficiency and scalability.
For example, the company uses Salesforce for customer relationship management, Workday for human resources, and AWS for computing and storage. By leveraging an iPaaS solution such as MuleSoft or HexaSync, they can effortlessly integrate these disparate systems, enabling automatic data synchronization, streamlined operations, and enhanced decision-making capabilities.
How to adopt cloud integration?
Adopting cloud integration involves evaluating business needs, selecting appropriate cloud services and platforms, and implementing a strategic plan for seamless integration of cloud and existing IT infrastructure to enhance operational efficiency and innovation. You can implement cloud integration in two ways: using APIs and using data gateways.
Using APIs
Leveraging APIs for cloud integration enables seamless connectivity between cloud services and on-premise applications, facilitating data exchange and system interoperability. This approach simplifies workflow automation, improves data accessibility, and supports a unified IT ecosystem, allowing businesses to scale efficiently and embrace new technologies with minimal disruption. APIs are key to driving digital transformation by easing the integration of new features and services.
Using data gateways
Data gateways facilitate secure cloud integration by bridging on-premise data sources with cloud services, ensuring data integrity and compliance with security standards. Ideal for hybrid scenarios, they enable organizations to combine cloud scalability with on-premise data security, supporting a balanced integration strategy that enhances operational flexibility while maintaining data sovereignty.
Conclusion
Cloud integration unites cloud-based services and on-premise systems, enhancing data exchange, efficiency, and scalability. It supports various strategies like multi-cloud, hybrid models, iPaaS, APIs, and data gateways to meet diverse business needs. As a key component of digital transformation, cloud integration drives innovation, optimizes resources, and secures a competitive edge in today’s digital landscape.